上篇博客提到了匹配的具体过程和相关优化,那么在匹配之后的事件该经过什么样的处理流程呢?
事件组合还原
在状态达到Final时,当前match被加入到potentialMatches中,标记为可能输出的match。SharedBuffer通过最后一个match不断向前追溯,利用版本号和NodeId(见上篇博客)形成独一无二的事件路径链。具体代码如下:
for (ComputationState match : potentialMatches) {
// 因为要从EventId还原到具体的T类型事件,做缓存提高效率
Map<EventId, T> eventsCache = new HashMap<>();
// 从SharedBuffer中,根据match的上一个NodeId和版本不断向前提取事件
Map<String, List<T>> materializedMatch =
sharedBuffer.materializeMatch(sharedBuffer.extractPatterns(
match.getPreviousBufferEntry(),
match.getVersion()).get(0),
eventsCache);
// 释放已经匹配完成的Node
sharedBuffer.releaseNode(match.getPreviousBufferEntry());
}
其中Map<String, List
之后在AbstractKeyedCEPPatternOperator.java中可以看到在匹配(nfa.process)结束之后,返回数据类型为 Collection<Map<String, List<IN>>,其中String表示的是状态名,List<IN>表示该状态匹配到的事件。具体代码如下:
/**
* Process the given event by giving it to the NFA and outputting the produced set of matched
* event sequences.
*
* @param nfaState Our NFAState object
* @param event The current event to be processed
* @param timestamp The timestamp of the event
*/
private void processEvent(NFAState nfaState, IN event, long timestamp) throws Exception {
Collection<Map<String, List<IN>>> patterns =
nfa.process(partialMatches, nfaState, event, timestamp, afterMatchSkipStrategy);
processMatchedSequences(patterns, timestamp);
}
processMatchedSequences的相关作用见下个标题。
事件输出
以CEPITCase.java的测试举例:
CEP.pattern(input, pattern).select(
new PatternSelectFunction<Event, String>() {
@Override
public String select(Map<String, List<Event>> pattern) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
// 对builder的一些操作
return builder.toString();
}
}
);
可以看到processMatchedSequences其实是直接调用了用户自定义的提取方法,Flink本身支持多种如flatSelect/select。
AfterMatchSkipStrategy
还有一个很有趣的功能是AfterMatchSkipStrategy,巧妙地运用这个功能可以帮助你过滤大部分无效匹配,或是业务上不需要的匹配。
假设你期望捕获股票中的W走势,如图:
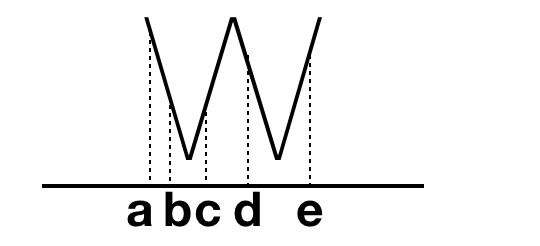
那么你会发现,acde和bcde都满足你说设置的W走势,那么你期望将他们全部输出吗?不一定。所以引入了AfterMatchSkipStrategy的功能,在你某个match匹配成功后,它会根据你所设定的清除规则,清除掉已经匹配成功或者还正在匹配的一些match。具体的接口如下:
/**
* Prunes matches/partial matches based on the chosen strategy.
*
* @param matchesToPrune current partial matches
* @param matchedResult already completed matches
* @param sharedBuffer corresponding shared buffer
* @throws Exception thrown if could not access the state
*/
public void prune(
Collection<ComputationState> matchesToPrune,
Collection<Map<String, List<EventId>>> matchedResult,
SharedBuffer<?> sharedBuffer) throws Exception {
// 挑选出开始prune的EventId(或者说位置)
EventId pruningId = getPruningId(matchedResult);
if (pruningId != null) {
List<ComputationState> discardStates = new ArrayList<>();
// 针对每一个已经匹配成功的match做检查
for (ComputationState computationState : matchesToPrune) {
if (computationState.getStartEventID() != null &&
shouldPrune(computationState.getStartEventID(), pruningId)) {
sharedBuffer.releaseNode(computationState.getPreviousBufferEntry());
discardStates.add(computationState);
}
}
matchesToPrune.removeAll(discardStates);
}
}
其中getPruningId和shouldPrune都是自定义AfterMatchSkipStrategy需要实现的接口。
/**
* Tells if the partial/completed match starting at given id should be prunned by given pruningId.
*
* @param startEventID starting event id of a partial/completed match
* @param pruningId pruningId calculated by this strategy
* @return true if the match should be pruned
*/
protected abstract boolean shouldPrune(EventId startEventID, EventId pruningId);
/**
* Retrieves event id of the pruning element from the given match based on the strategy.
*
* @param match match corresponding to which should the pruning happen
* @return pruning event id
*/
protected abstract EventId getPruningId(Collection<Map<String, List<EventId>>> match);
常见的预定义策略有如下几种: